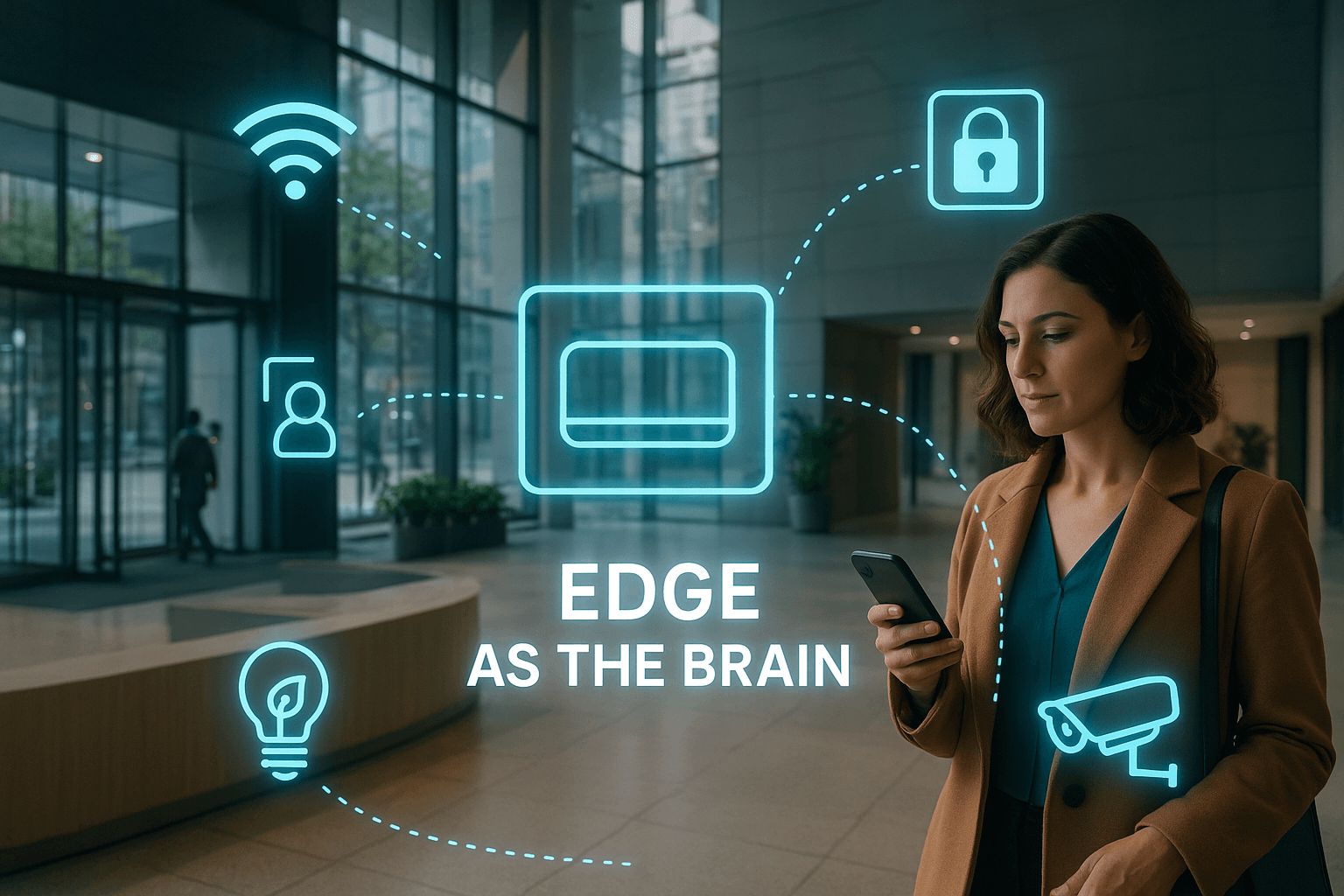
The best way of Monetizing WiFi Infrastructure in Africa: A Path to Sustainability and Growth
Monetizing WiFi Infrastructure in Africa: A Path to Sustainability and Growth

Introduction
WiFi infrastructure in Africa has experienced significant growth, with the prevalence of Wi-Fi hotspot services expanding rapidly across the continent. However, many of these hotspots face challenges in maintaining sustainability, as they primarily rely on charging users for internet usage alone. To ensure long-term success, a more innovative and multi-faceted approach to monetizing WiFi infrastructure is crucial. This article explores the potential for monetizing WiFi infrastructure in Africa through the adoption of edge computing and the provision of additional services beyond internet access.
1. The Limitations of Traditional Monetization Models
Traditional monetization models for WiFi hotspots often rely solely on charging users for internet access. This approach can exclude individuals who cannot afford to pay, resulting in a limited customer base and reduced revenue potential. To overcome these limitations, a more comprehensive approach is needed.
2. The Role of Edge Computing in Monetizing WiFi Infrastructure
Integrating edge gateways with WiFi capability can transform WiFi infrastructure into multi-purpose platforms. In addition to providing internet services, these gateways offer storage and computing power to third-party businesses. This expanded functionality allows for the creation of new revenue streams and enhances the sustainability of the WiFi infrastructure.
3. Benefits of Multi-Purpose WiFi Infrastructure
a) Increased Revenue Streams: Incorporating edge computing enables businesses to charge for access to additional computing resources, attracting new revenue streams beyond internet usage fees. Research indicates that the global edge computing market is growing rapidly, further emphasizing the potential for increased revenue through this approach.
b) Free Internet Access to Boost Customer Base: Offering free Internet access to users can expand the customer base and foster positive brand associations within the community. By providing additional services beyond internet access, companies can offset the cost of providing connectivity and generate more revenue through the sale of these supplementary services.

Check out my other article The future of digital infrastructure.
4. Challenges and Considerations
a) Cost of Infrastructure: Building and maintaining a multi-purpose WiFi infrastructure entails significant investments in hardware, software, and ongoing maintenance. Companies must carefully evaluate the financial feasibility and long-term profitability of such ventures.
b) Regulatory Compliance: Meeting regulatory requirements, such as obtaining licenses and approvals to operate edge gateways, can pose challenges. Companies need to navigate the legal landscape and ensure compliance to avoid potential roadblocks.
5. The Potential for Sustainable Growth
By adopting a multi-purpose approach and incorporating edge computing, companies can monetize WiFi infrastructure in Africa effectively. This approach enhances revenue opportunities, ensures a wider customer base through free internet access, and fosters a sustainable digital infrastructure for local communities. The long-term benefits outweigh the challenges, making the monetization of WiFi infrastructure a compelling business opportunity in Africa.
Conclusion
To achieve sustainable growth and monetize WiFi infrastructure in Africa, companies must move beyond traditional monetization models and embrace a multi-purpose approach. Incorporating edge computing and offering additional services beyond internet access can create new revenue streams, expand the customer base, and foster a robust digital ecosystem. With careful planning, companies can successfully monetize WiFi infrastructure, make a positive impact on the digital landscape, and contribute to the sustainable growth of Africa’s connectivity infrastructure.